
What Is Multicasting Routing. A multicast packet may have destinations in more than one network. A host may join some new groups and. 85 Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol DVMRP DVMRP is a distance vector protocol like the routing information protocol RIP for unicast routing. Through the process of multicasting the communication and processing overhead of sending the same data packet or data frame in minimized.
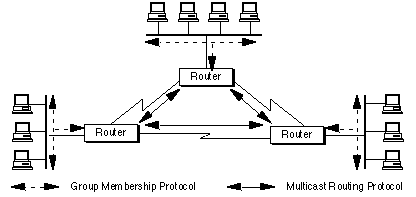
Fast possible to all members of the multicast group. Membership in the group does not have any relation to the prefix associated with the network. It supports one to many and many to many data transmission across LANs or WANs. The membership is not a fixed attribute of a host. A multicast packet may have destinations in more than one network. While the multicast routing algorithms we have studied above construct a single shared routing tree that is used to route packets from all senders the second broad class of multicast routing algorithms construct a multicast routing tree for each source in the multicast group.
85 Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol DVMRP DVMRP is a distance vector protocol like the routing information protocol RIP for unicast routing.
The membership is not a fixed attribute of a host. Protocol Independent Multicast PIM is the most important Multicast Routing Protocol. Membership in the group does not have any relation to the prefix associated with the network. The regulation of routing in multicasting understood as the transport of multicast packets by routers and networks is responsible for unique routing protocols that work with various algorithms that forward the data flow most efficiently and efficiently. The Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol DVMRP is a distance-vector routing protocol and Multicast OSPF MOSPF is an extension to the OSPF link-state unicast routing protocol. Its very useful for streaming media so lets explore how this works.