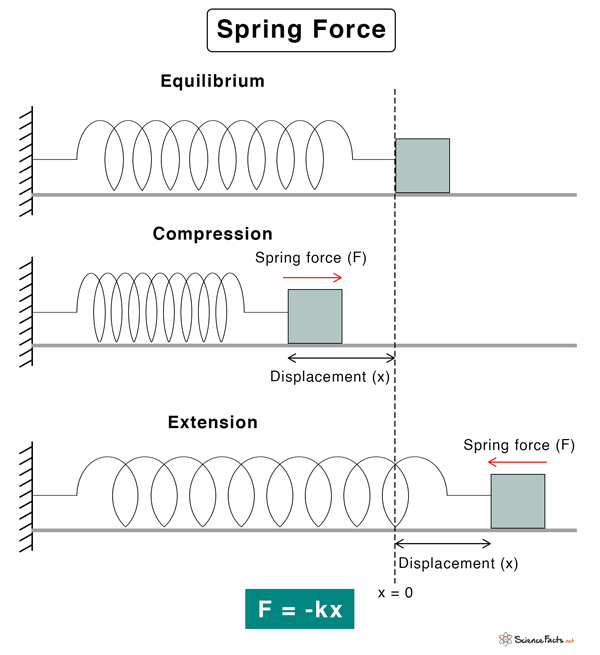
What Is A Spring Force. As a result it experiences a restoring force that tends to retract the spring back to its original position. This video introduces the Spring Force as used in Physics. Hookes law is a law of physics that states that the force F needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance x scales linearly with respect to that distancethat is Fs kx where k is a constant factor characteristic of the spring ie its stiffness and x is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. A spring is an object that can be deformed by a force and then return to its original shape after the force is removed.
It is a contact force that can be found in elastic materials. It is a characteristic of the material at a molecular level and its three-dimensional shape on a macro level. Since k is a constant the relationship between force and distance is linear. The spring scale is measured in Newtons. The force exerted by a spring on objects attached to its ends is proportional to the springs change in length away from its equilibrium length and is always directed towards its equilibrium position. That is the change in length from the springs relaxed natural or original length x0.
It is a contact force that can be found in elastic materials.
In other words the spring force always acts so as to restore mass back toward its equilibrium position. Force spring force elastic force applied force deforming force. In other words the spring force always acts so as to restore mass back toward its equilibrium position. When a metal spring is stretched or compressed it is displaced from its equilibrium position. One end is fixed and a particle-like object say a block is attached to the other free end. A higher spring constant means a stiffer spring thats harder to stretch because for a given displacement x the resulting force F will be higher while a looser spring thats easier to stretch will have a lower spring constant.
