Structural Abnormalities Of Axial Skeleton. Development of the Skull. Structure of Bone Tissue. Knowledge of the developmental processes that give rise to the skeleton is important for understanding the abnormalities that may arise in skeletal structures. To investigate abnormalities in the skeleton with the exclusion of the skull cervical spine hands and feet in patients with Laron syndrome who have an inborn growth hormone resistance and congenital insulin-like growth factor-1 IGF-1 deficiency.
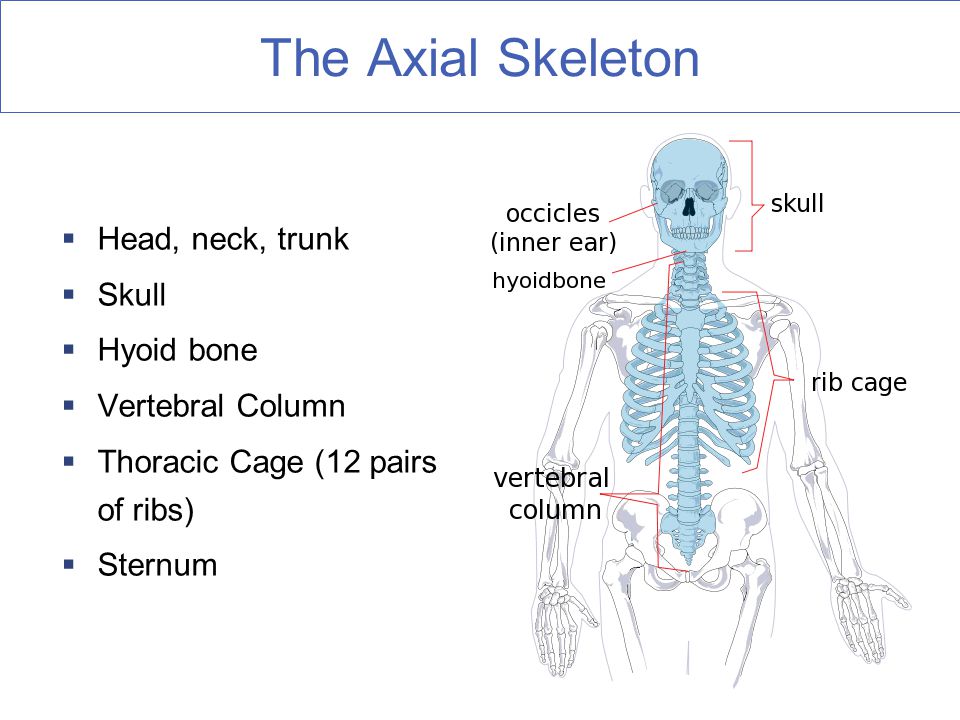
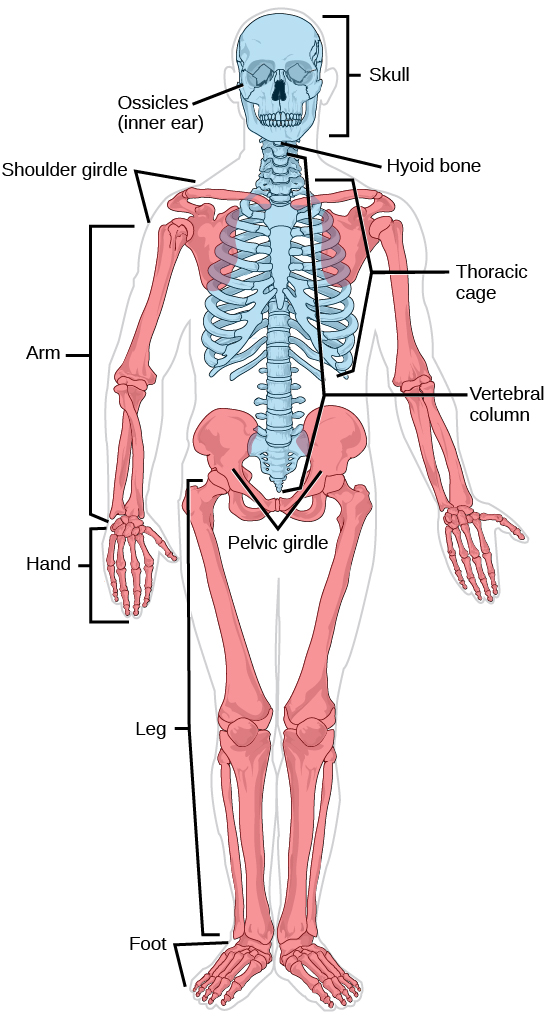
Development of the Skull. The function of the axial skeleton is to provide support and protection for the brain spinal cord and organs in the ventral body. Stenosis of Lumbar Spine-narrowing of vertebral canal in lumbar region. The function of the axial skeleton is to provide support and protection for the brain the spinal cord and the organs in the ventral body cavity. The axial skeleton begins to form during early embryonic development. The three most commonly occurring are developmental dysplasia of the hip cleft palate cleft lip and palate.
Ankylosis of several of the joints causes structural abnormalities of the axial skeleton.
1 Neck pain is also highly prevalent. Stenosis of Lumbar Spine-narrowing of vertebral canal in lumbar region. Skeletal abnormalities commonly begin during stage 6 and 7 when the majority of the vertebral elements are ossifying. During the third week of embryonic development a rod-like structure called the. The skull 22 bones also the ossicles of the middle ear the hyoid bone the rib cage sternum and the vertebral columnThe axial skeleton together with the appendicular skeleton form the complete skeleton. The axial skeleton begins to form during early embryonic development.