Starting Problem In Supersonic Inlets. If the crews attempts to restart the inlets supersonic flow failed they would have to slow their aircraft to subsonic speeds. Wind tunnels which can generate the required uniform supersonic flows are commonly used in inlet experiments. Stable operation no drastic inlet property changes for small changes in flight conditions Supersonic Inlets - 2 AE4451 Propulsion Copyright 2006 2017 by Jerry M. Boundary-layer bleed in supersonic inlets is typically used to avoid separation from adverse shock-waveboundary-layer interactions and subsequent total pressure losses in the subsonic diffuser.

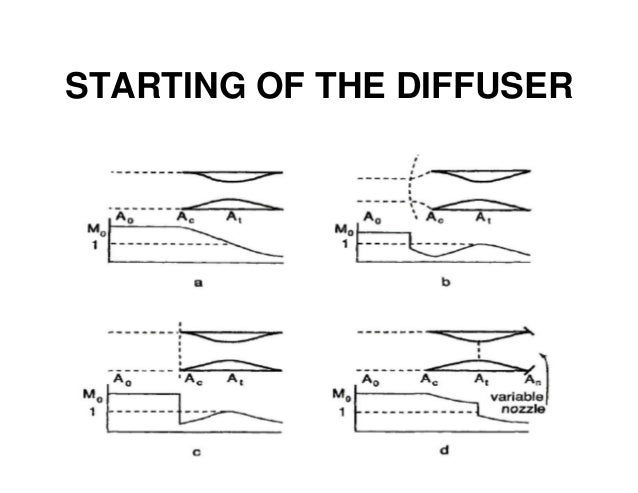
With a top speed of Mach 16 the Lockheed Martin F-35 Joint Strike Fighter has an inlet design that is far simpler than that of the Mach 3-plus SR-71. Diffuser lowest potential p o loss but starting problem overspeeding and single design M flight or var. Starting can be defined as a stable condition in which the flow is supersonic at the cowl inlet lip and the terminal normal shock wave is located downstream of the inlet throat ie the minimum cross-sectional area of the inlet duct. In aircraft engine intakes. Unstart of the wind tunnel is the reverse process. The normal shock occurs ahead of the cowl lip.
CFD Modeling of the Hypersonic Inlet Starting Problem.
During the initial phase of the mission the missile. With a top speed of Mach 16 the Lockheed Martin F-35 Joint Strike Fighter has an inlet design that is far simpler than that of the Mach 3-plus SR-71. The shock waves that develop during the starting or unstart process may be visualized with schlieren or shadowgraph optical techniques. In aircraft engine intakes. FLOW INSTABILITY BUZZ Buzz is an airflow instability caused by the shock waves rapidly being alternately swallowed and expelled at the inlet of the duct and occurs in supersonic intakes at subcritical operations. Unstart of the wind tunnel is the reverse process.