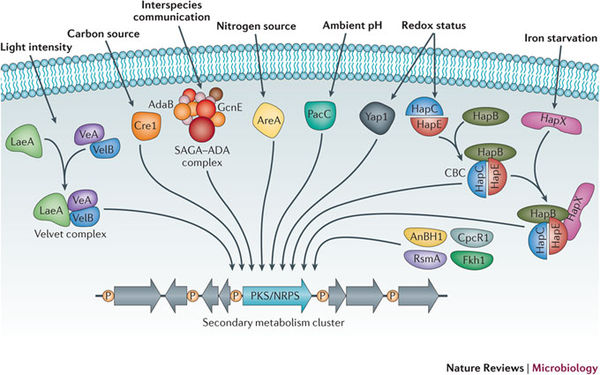
Primary Metabolism Of Fungi. Their primary metabolism is a significant source of industrially important compounds as well as of monomeric building blocks for the production of secondary metabolites and extracellular enzymes. In fungal genomes the genes involved in these metabolic pathways can be physically linked on chromosomes forming gene clusters. Much of the ecological success of the filamentous fungi in colonizing the planet is owed to their ability to deploy their secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites are considered essential to microorganisms for proper growth.
Unlike primary metabolites these. Some of the solid substrates utilized by fungi are dead and decaying material including herbivore dung saprophytic and coprophilous fungi live plants endophytic parasitic and mycorrhizal fungi lichens lichenicolous and endolichenic fungi and insects entomopathogenic fungi. Chapter 5 Why Study Metabolism. Secondary metabolites do not play a role in growth development and reproduction and are formed during the end or near the stationary phase of growth. Particular examples include reacting to extracellular stimuli producing precursor molecules required for cell division and morphological changes as well as providing monomer building blocks for production of secondary metabolites and extracellular enzymes. Primary metabolism affects all phenotypical traits of filamentous fungi.
Primary metabolism affects all phenotypical traits of filamentous fungi.
Fungi are important primary decomposers of organic material as well as amazing chemical engineers synthesizing a wide variety of natural products some with potent toxic activities including antibiotics and mycotoxins. With their versatile metabolism fungi break down organic matter which would not otherwise be recycled. View page-32pdf from LS P127 at Queensland University of Technology. Filamentous fungi have been described to produce a great variety of volatile metabolites belonging to saturated hydrocarbons alcohols aldehydes ketones lactones linear esters ethers phenols and terpenoids. Chapter 5 Why Study Metabolism. These aspects are referred to as primary metabolism.