Microwave Sensors In Remote Sensing. Microwave remote sensing can be used to estimate soil moisture on the basis of large contrast that exists between the dielectric constant values for dry and wet soils. Bhattacharya 13 Microwave radiometers Measure the emittance of EM energy within the microwave region of the EM spectrum just like thermal IR sensors Non-imaging RADARs 1. Microwave remote sensing is a rapidly developing discipline with an increasing number and diversity of specialised sensors Its foundation is the electromagnetic theory Microwave data should not be treated as images but as measurements Visual metaphors dominate the remote sensing literature but for microwaves an audio metaphor is more appropriate. Microwave sensor functions as occupancy sensor like PIR sensor.
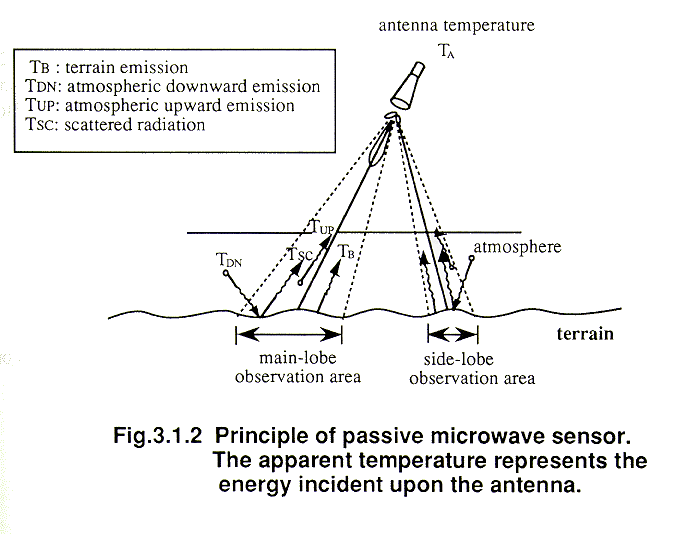
The passive sensors include radiometers both imaging and non-imaging types. The reason for this is because physically speaking the microwave signals can easily penetrate clouds are independent of daylight and remain largely unaffected by rain. This is detected by the sensor to take appropriate action. Our mission is to provide research-quality geophysical data to the global scientific community. Active Microwave Remote Sensing. Active Passive sensors Remote sensors create their own electromagnetic energy that is transmitted from the sensor towards the terrain interacts with the terrain producing a backscatter of energy and is recorded by the remote sensors receiver.
This paper reviews the potential of applications of microwave remote sensing of soil moisture and vegetation for agricultural application.
The quantity also depends on the illumination angle and the. This is detected by the sensor to take appropriate action. The active type receives the backscattering which is reflected from the transmitted microwave which is incident on the ground surface. Synthetic aperture radar SAR microwave scatterometers radar altimeters etc. Introduction to Satellite Remote Sensing 2017. The reason for this is because physically speaking the microwave signals can easily penetrate clouds are independent of daylight and remain largely unaffected by rain.