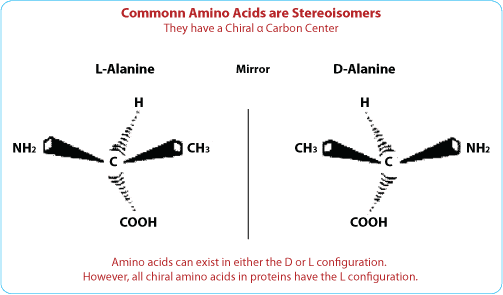
L Vs D Amino Acids. L is the left winding amino acid and D is the right winding amino acid. D- amino acids are found as constituents of natural peptides produced primarily by microorganisms using a non-ribosomal mechanism of synthesis. Most amino acids fall into the S configuration but cysteine is an R because the sulfur atom has higher priority. Their C_alpha chiral center is the L-enantiomer based on the structural comparison with L-glyceraldehyde.

Human amino acids have been found to be the L type and this is usually the preferred supplement as well. Very low MIs. L-forms of amino acids tend to be tasteless whereas D-forms tend to taste sweet. However cysteine is still an L and the amine would still appear on the left in the Fischer Projection. The two smell different. Their C_alpha chiral center is the L-enantiomer based on the structural comparison with L-glyceraldehyde.
To attempt to avoid confusion the optical activities are given as for dextrorotatory and - for levorotatory.
Most amino acids fall into the S configuration but cysteine is an R because the sulfur atom has higher priority. ICOD of D-one is more stable than the L-one and then evidence boiling or melting point of it. This is why biologists stick to D and L for amino acids. All common amino acids are the L-enantiomer ie. Very low MIs. L and D amino acids - YouTube.