High Strain Rate Material Properties. Common applications where the high strain rate properties are critical are composite and steel material properties in high speed crash analysis of automotive and aerospace structures high speed ballistic impacts and drop impacts of consumer durables and electronic items. In addition large variation exists in the reported material properties in literature. As the temperature was reduced the amount. In the range of high strain rates the mechanical behaviour of materials is characterized by an increased strain rate sensitivity by increasing effects of mass inertia forces and by the adiabatic.

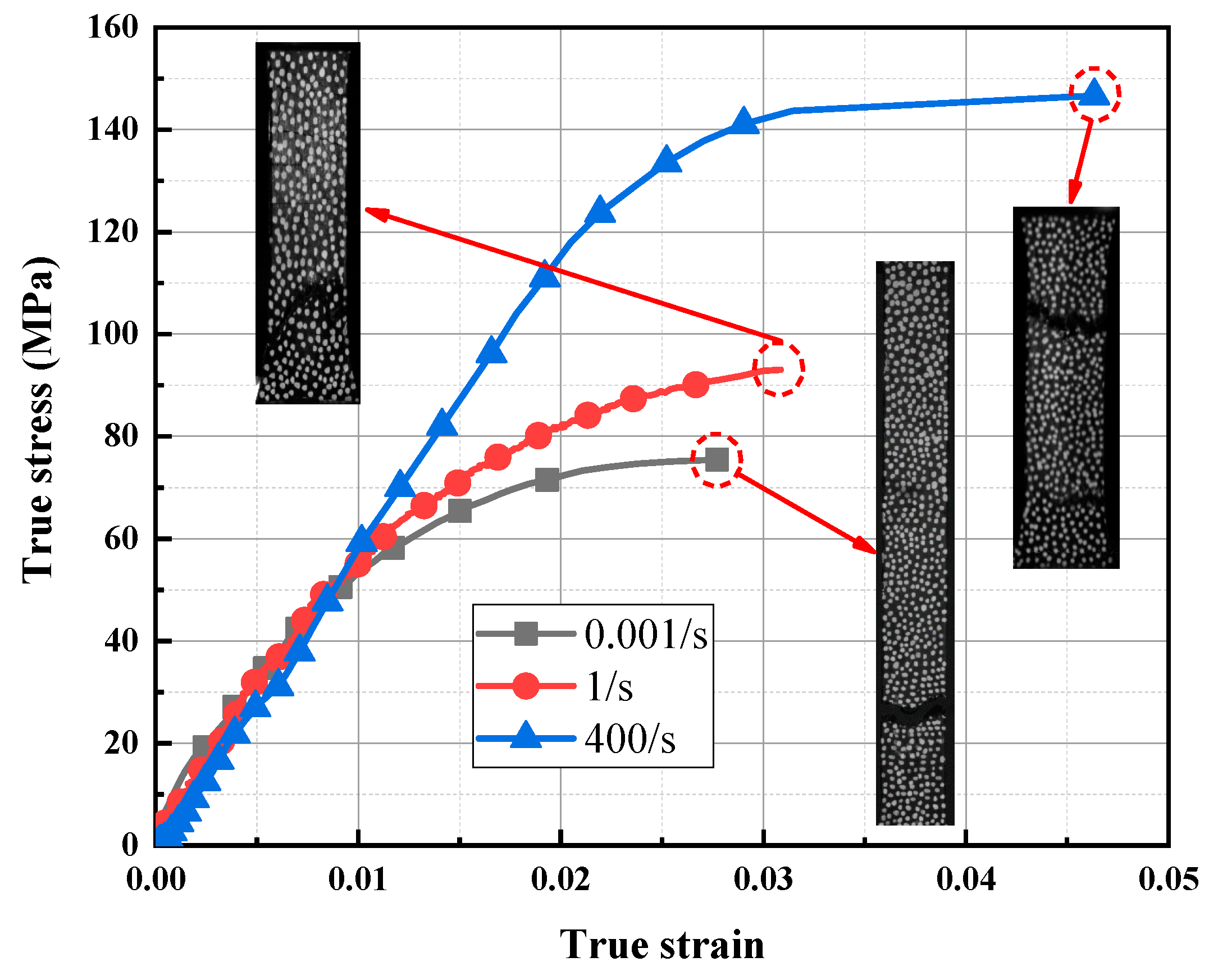
While most materials become stronger and more ductile at high strain rate others on the contrary may become weaker and more brittle Stavrogin Tarasov 2001. The high strain rates vary from 250-1100s. These parameters are particularly valuable for crash simulations. For example the storage and loss moduli from oscillatory shear tests demonstrate orders of. The yield criterion which governs the plastic flow was assumed to be independent of the rate of strain dot varepsilon. For geomaterials such as concrete.
As the temperature was reduced the amount.
For example the storage and loss moduli from oscillatory shear tests demonstrate orders of. The tests show that changing the fiber orientation changes the values of the ultimate strength and strain of the IM78551-7 graphiteepoxy composite. High-speed tensile tests provide characterization of the tensile properties of metals or plastics at high strain rates. The influence of increasing strain rate on the mechanical behavior and deformation substructures in metals and alloys that deform predominately by slip is very similar to that seen following quasi-static deformation at increasingly lower temperatures or due to a decrease in stacking-fault energy γ sf. This TWIP steel had a moderate strain hardening and dislocation glide was the main deformation mechanism. Other amorphous materials such as bulk metallic glasses amorphous glassy carbon etc.