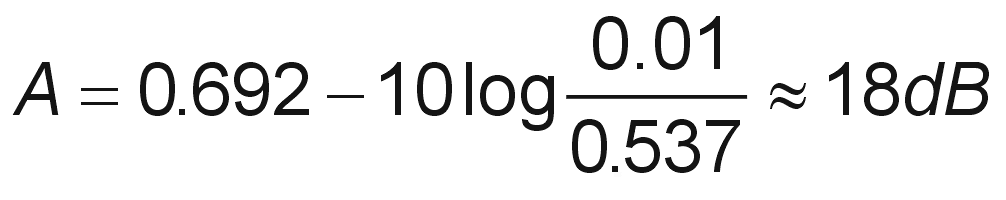
Fade Margin In Microwave. In general the longer the link the more fluctuation in signal levels and the greater the fade margin needs to be. First decide on a propagation reliability PR over time. CFM is the Composite Fade Margin. Flat fading A fade where all frequencies in the channel are equally affectedThere is barely noticeable variation of the amplitude of the signal across the channel bandwidth If necessary flat fade margin of a link can be improved by using larger antennas a higherpower microwave transmitter lower loss feed line and splitting a longer path into two shorter hops On water paths at frequencies.

Then it is explained how to determine link availability from the calculated FM. Planning a Microwave Link. So called because it provides a margin of safety in the event of a temporary. Determining sufficient fade margin is the most important step in microwave link design. CFM is the Composite Fade Margin. Flat fading A fade where all frequencies in the channel are equally affectedThere is barely noticeable variation of the amplitude of the signal across the channel bandwidth If necessary flat fade margin of a link can be improved by using larger antennas a higherpower microwave transmitter lower loss feed line and splitting a longer path into two shorter hops On water paths at frequencies.
Quality and availability calculations.
EIFM is the External Interference Fade Margin. Dispersive Fade Margin DFM is the contribution to outage that accounts for in-band distortion that can at times cause. In general the longer the link the more fluctuation in signal levels and the greater the fade margin needs to be. Fading and fade margins calculations. Method is given for the fade margin FM of the links by using radio equipment parameters and system gain SG. So called because it provides a margin of safety in the event of a temporary.