
Enzyme Substrate Complex Labeled. Label the pertinent features of the figure showing how an enzyme functions. Enzymes also promote chemical reactions by bringing. The addition of a non-competitive inhibitor will prevent the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex. Spondto crosslinked enzyme-substrate complex.
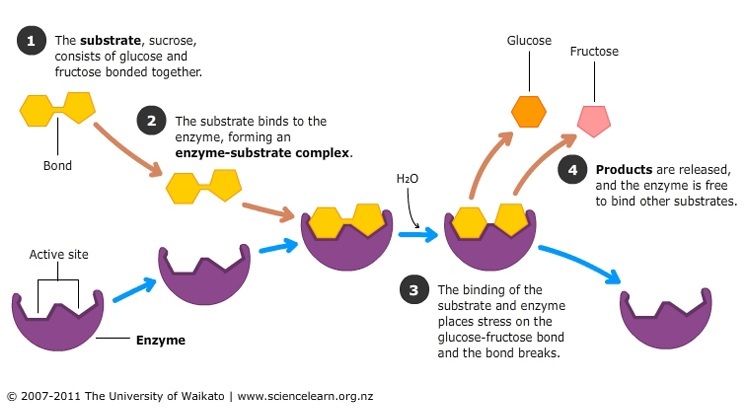
Draw and label the enzyme products and active site after enzymatic action. This complex lowers the activation energy of the reaction and promotes its rapid progression by providing certain ions or chemical groups that actually form covalent bonds with molecules as a necessary step of the reaction process. For example the enzyme acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the decomposition of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to choline and acetic acid. This flexible model allows the enzyme to modify its conformation when in contact with the substrate adapting to it and orienting essential residues to obtain the optimal conformation to form the ES complex. Draw a labelled diagram based on relevant molecules selected from the diagram above to explain how this occurs. Enzymes are highly specific catalysts for biochemical reactions with each enzyme showing a selectivity for a single reactant or substrate.
Lock and key model Enzymes are folded into.
In the case of more than one substrate these may. The highly complex organization of living systems requires constant input of energy and the exchange of macromolecules. Enzymes are substances that play a crucial role in carrying out biochemical reactions. Many enzymesubstrate reactions follow a simple mechanism that consists of the initial formation of an enzymesubstrate complex ES which subsequently decomposes to form product releasing the enzyme. The activity of an enzyme is influenced by certain aspects such as temperature pH co-factors activators and inhibitors. The substrate is transformed into one or more products which are then released from the active site.