
Circular Economy Core Principles And Concepts. The 4 principles of the Circular Economy. Preservation of ecological diversity is a core source of resilience for the planet. Keep products and materials in use. Circular Economy historical origins overall principles and concepts.
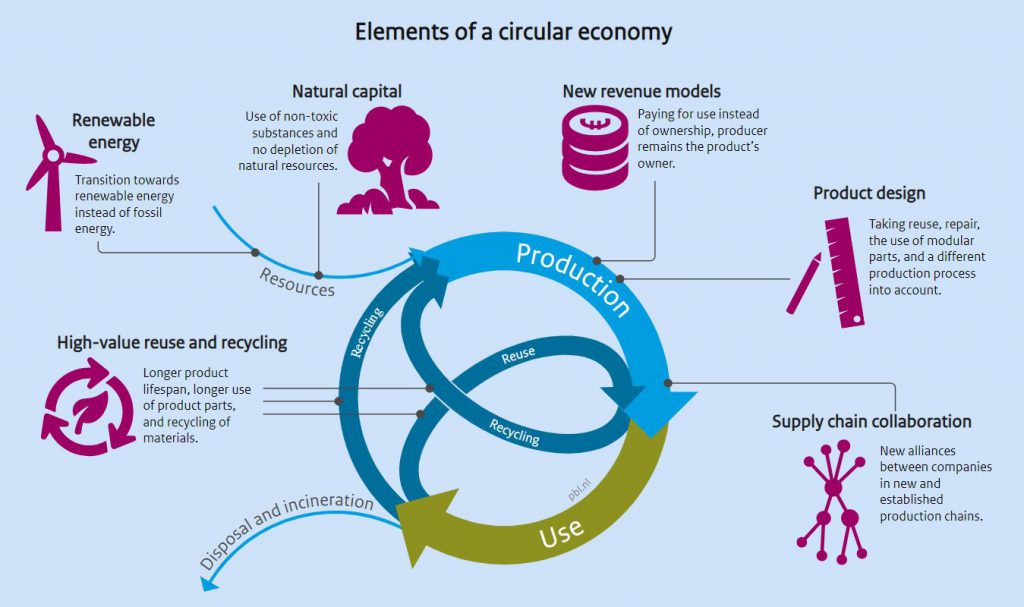
A core principle of acting within a circular economy is to preserve complexity. The core elements of the circular economy relate to direct circular handling of material and energy flowsfor example closing loops extending product lifecycles and increasing usage intensity. Described as an economy with a closed-resource loop Wautelet 2018 a circular economy encourages the rematerialization and reuse of waste with the aim to decouple economic growth from finite. The current global economy is built on a take-make-waste industrial model and. Complexity feedback Systems optimisation Tipping points and Unintended consequences. Material and energetic losses are tolerated for the sake of preservation of biodiversity.
Since the invention of the steam engine in the 1600s global manufacturing has.
The concept suggests the minimization of waste and pollution by reducing damages. It is a much higher priority. Principles of Circular Economy 1 Minimization of waste and pollution. As described by De Rosnay natural systems are self-regulating rich in feedback loops resilient and optimised Dixon 2011De Rosnay 1979. This principle stands for the continuous cycling of materials and products. A core principle of acting within a circular economy is to preserve complexity.