
Amino Acid Group Structure. Compare with the simplest of the amino acids glycine which has only H as an R-group. Each amino acid has at least one amine and one acid functional group as the name implies. They differ from each other in their side-chain called R group. The term amino acid is short for α-amino alpha-amino carboxylic acid.
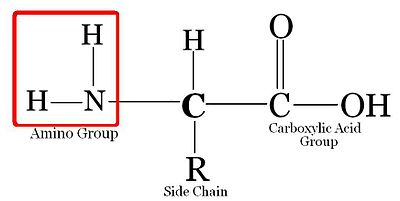
An amino acid is an organic molecule that is made up of a basic amino group NH 2 an acidic carboxyl group COOH and an organic R group or side chain that is unique to each amino acid. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure which consists of a central carbon atom also known as the alpha α carbon bonded to an amino group NH 2 a carboxyl group COOH and to a hydrogen atom. Thus amino acids are the basic unit of. Amino acids differ from each other with respect to their side chains which are referred to as R groups. It is the R-group or side chain that differs between the 20. These 4 groups are.
They differ from each other in their side-chain called R group.
There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids and all have common structural features an amino group -NH3 a carboxylate -COO- group and a hydrogen-bonded to the same carbon atom. General Structure of Common Amino Acids General structure of amino acidsgroup and a variable side chain Side chain determines. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure which consists of a central carbon atom also known as the alpha α carbon bonded to an amino group NH 2 a carboxyl group COOH and to a hydrogen atom. The different properties result from variations in the structures of different R groups. All amino acids have a central carbon atom surrounded by a hydrogen atom a carboxyl group COOH an amino group NH2 and an R-group. They are distinguished by the attached functional group R.